This article gives an overview of the components used in analog electronics. Electronic components are linked together to form an electronic circuit to perform a certain function.
There are two main families of components: passive components and active components. Active components require electrical power and can amplify a voltage or current signal.
Passive components
Resistance
Resistors are passive components made of carbon or metal, commonly used in electronics. Its primary function is to limit the current in an electrical circuit. It can therefore protect other components.
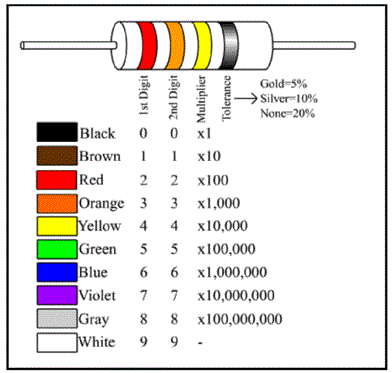
Example of function and use
- Limits electrical current (brightness control or protection)
- Divides voltage (voltage divider bridge)
- Stabilizes electrical current (signal filtering)
Capacitor
A capacitor is used to store electrical charges. It consists of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. They are used to stabilize a power supply, filter signals and separate alternating and direct current.
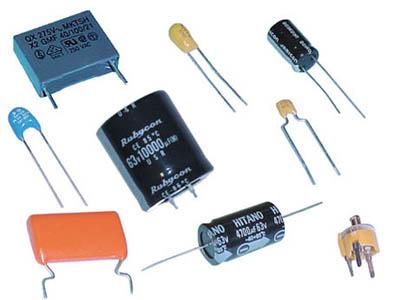
Example of function and use
- Stores and releases electrical energy
- Smoothes voltage variations
- Passes AC signals, blocks DC signals
Inductance
Inductances are used to store magnetic energy, capture waves or create a pulse, for filtering and their electromagnetic properties. They are also known as coils or solenoids.

Example of function and use
- Stores magnetic energy
- Filters signals by frequency
- Produces magnetic fields
Active components
Diode
The special feature of the diode is that it allows current to flow in only one direction. It is used, for example, to protect a power source or to convert alternating current into unidirectional current.
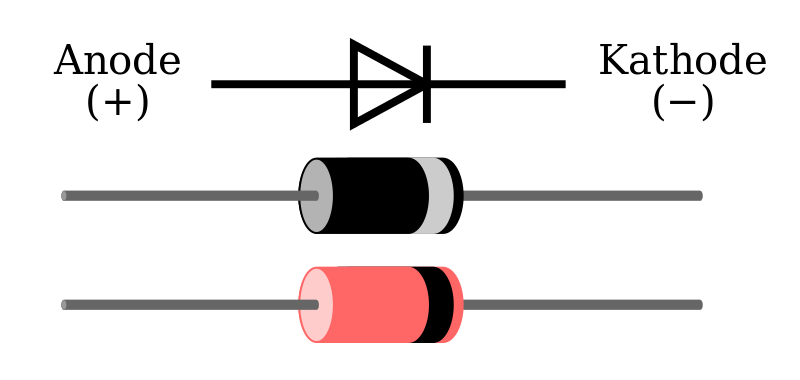
Example of function and use
- Allows current to flow in one direction only
- Converts AC to DC (rectification)
- Emits light in light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
Voltage regulator
Voltage regulators are used, as the name suggests, to modify the electrical voltage level. They are used to power components requiring a nominal voltage lower than the supply voltage.

Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor that modulates the current or voltage on its output electrode (collector or drain) by means of a signal on its control electrode (base or gate). It acts as a controlled amplifier or switch.
Example of function and use
- Electrical signal amplification
- Circuit switching
- Power control
Thyristor and triac
The thyristor operates on the same principle as the transistor, except that it acts as a switch for high voltages. Combining thyristors produces diac or triac.

Integrated circuits
Multiplexer
The multiplexer is used to transmit different signals through the same medium, selecting one input at a time.

Shift register
The shift register is an integrated circuit with memory registers for storing a high or low state and switching the corresponding output pin to high (5V) or low (0V). It is often used to increase the number of inputs and outputs on a microcontroller.
Diode bridge
A diode bridge is an assembly of diodes for full-wave current rectification. This means passing positive current and reversing the sign of negative current.
Interface components
Push button
The pushbutton is the basic element for sending information from an interface. When pressed or released, it sends information to a microcontroller.

LED
The LED (light-emitting diode) is a well-known component for receiving information from an interface. This component exists in various forms, such as the 5mm LED or the LED ribbon made up of addressable LEDs.

Display
Seven-segment displays, LCD screens, OLED screens or TFT screens are ideal for displaying comprehensive information and creating interfaces.
Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a variable resistor. It sends information according to the position of the knob.

Rotary encoder
A rotary encoder sends angle and direction information. It is usually fitted with a pushbutton, making it ideal for browsing a menu.

Actuators
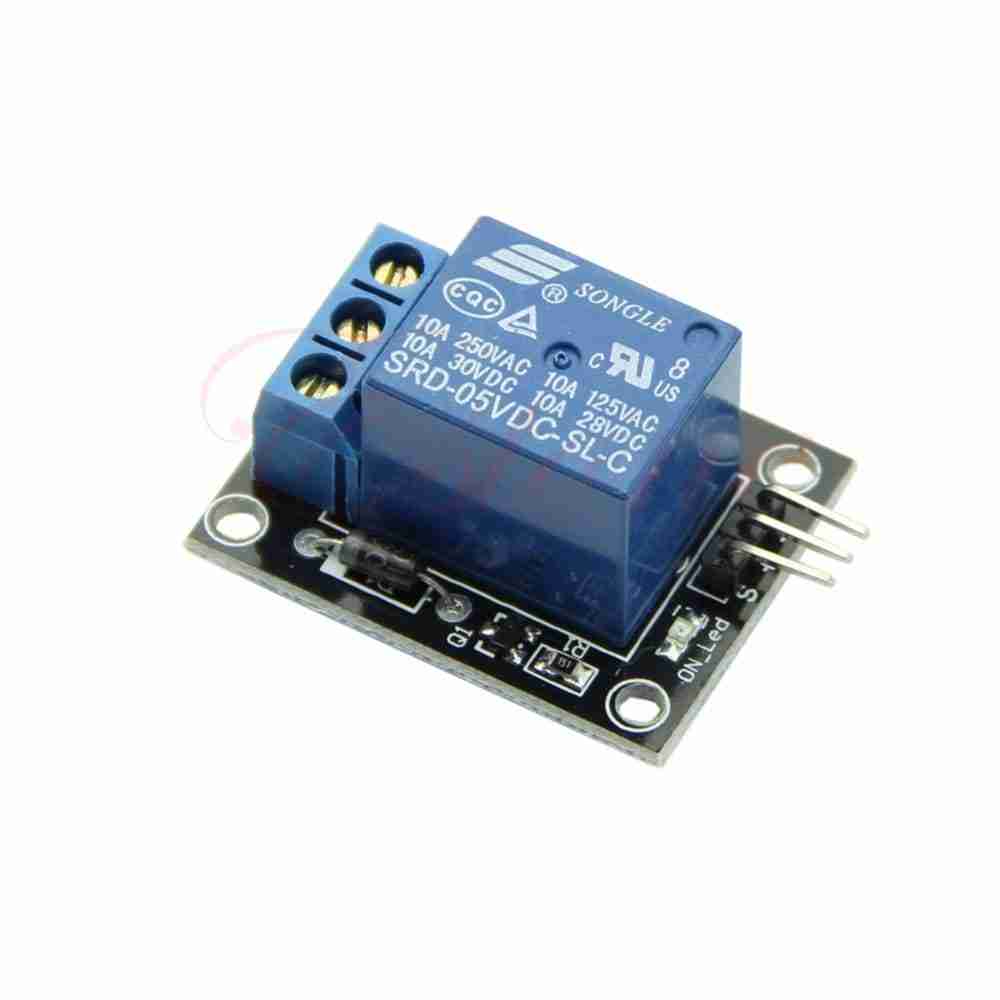
Relay
A relay is a controllable switch that opens or closes a contact depending on the state of its control pin. This component has the particularity of galvanically isolating the control part from the power part. As a result, it is often used to control power or AC circuits.

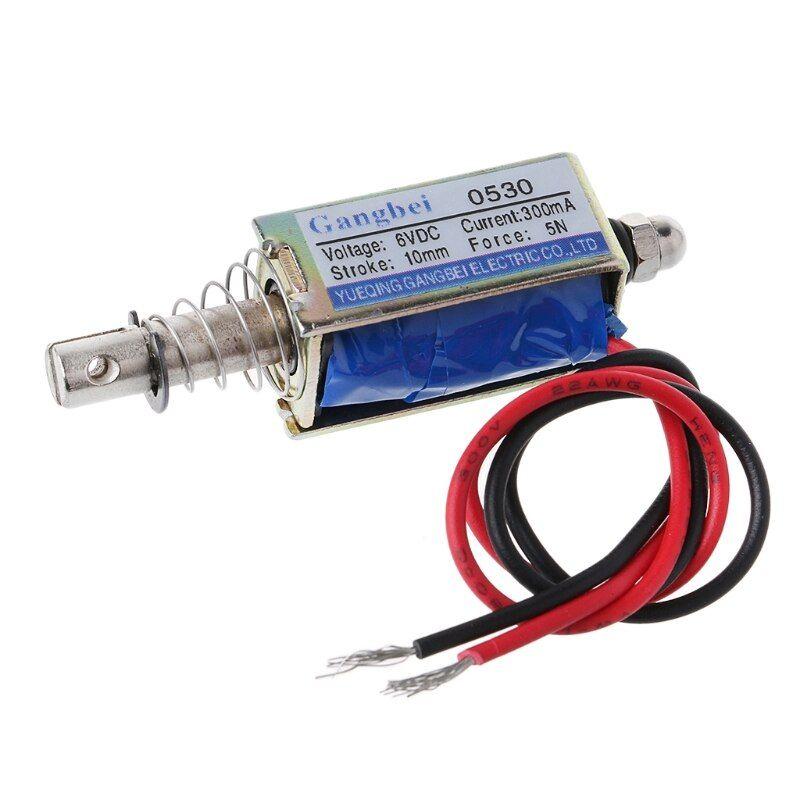
Electromagnet
An electromagnet consists of a coil and an iron core that transforms electrical power into linear motion.

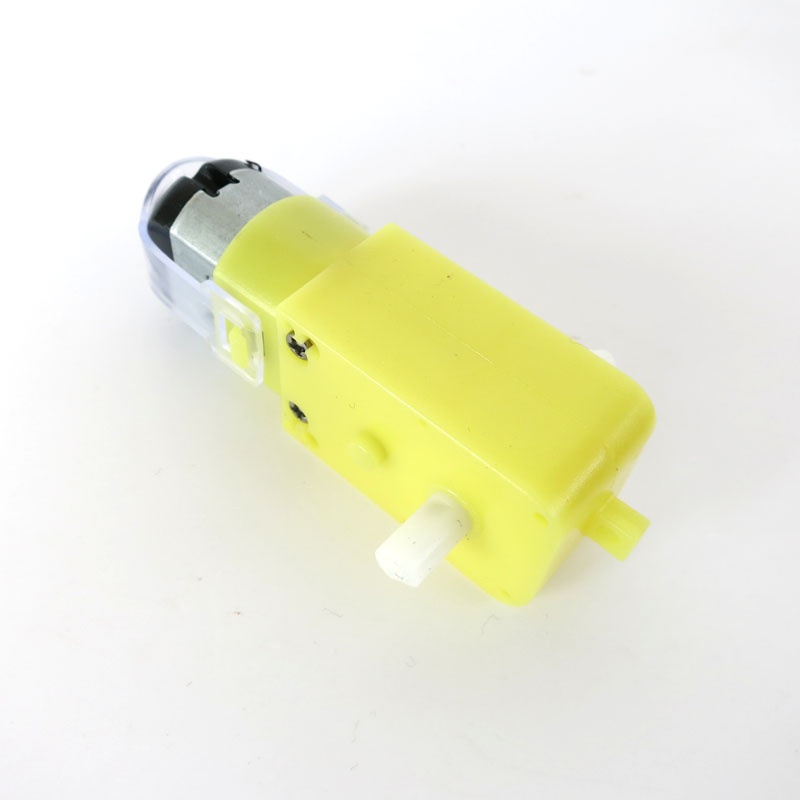
Motors
Electric motors are components that transform electrical power into motion. There are different types: DC motor, stepper motor, brushless motor

Digital components
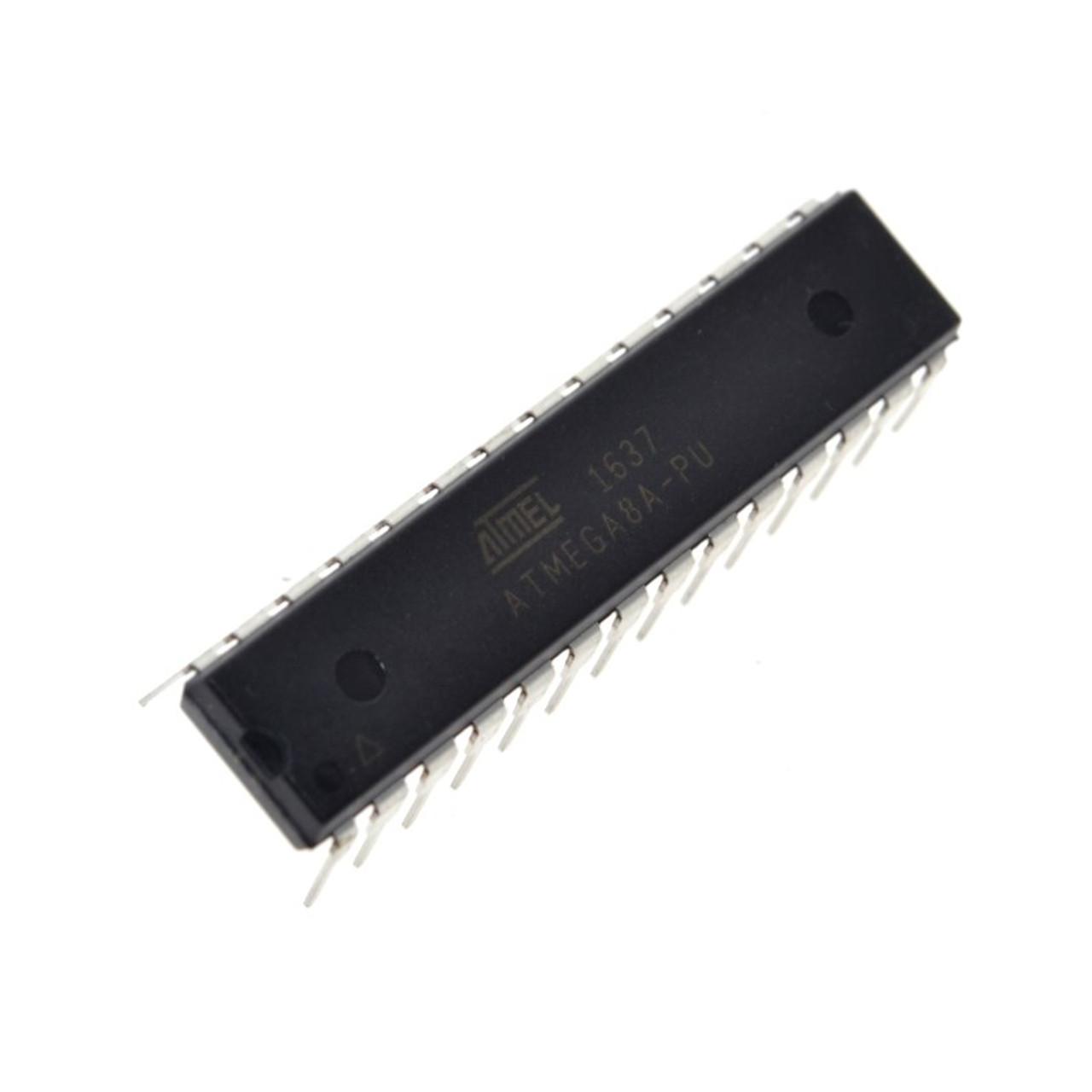
Microcontroller
The microcontroller is the basis of a computer: it consists of a processor, an I/O interface and a memory.

Microprocessor
The microprocessor is the component that executes the computer program.
Quartz
Quartz is a component that oscillates at a stable frequency when powered. This makes it an important component for creating the clock in digital electronics.

Memory
Memory is a digital electronic component used to store data.