It is possible to access a folder on a remote machine by installing a Samba server under Linux. This server lets you access a certain file folder from any machine connected to the same network.
Installing Samba
To install Samba,
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install samba -y
Check version
smbd --version
Before configuration, check that the Samba service is disabled.
sudo systemctl stop smbd
Configuring Samba under Linux
To share a folder securely, you need to enter certain information in the configuration file
sudo mv /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb.conf.bak
To modify the configuration file, you can use a text editor or nano in the terminal.
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
The information to enter is the path, which is the address of the folder to be shared. Don’t forget to replace with the user’s name. To obtain the user name, enter the command whoami
[smbSharedFolder] comment= Folder Shared by Samba Server path = /home/<USERNAME>/smbSharedFolder public = yes read only = no
Restart the Samba service
sudo systemctl restart smbd
To check the status of the service and that there are no errors in the configuration file
sudo systemctl status smbd
N.B.: Multiple shared folders can be created by adding a configuration block or section (starting with [sharefolder]) to the
Create and modify user rights
To access the Samba shared folder with your user account, you need to add it to the Samba group
sudo smbpasswd -a <username>The system then asks you to enter and confirm the user password.
Check user list
sudo pbdedit -L -v
Accessing the Samba folder from a remote machine
To access the folder from another computer, you need to know the IP address of the computer on which Samba is installed. To retrieve the IP address, enter the following command from a terminal
hostname -I
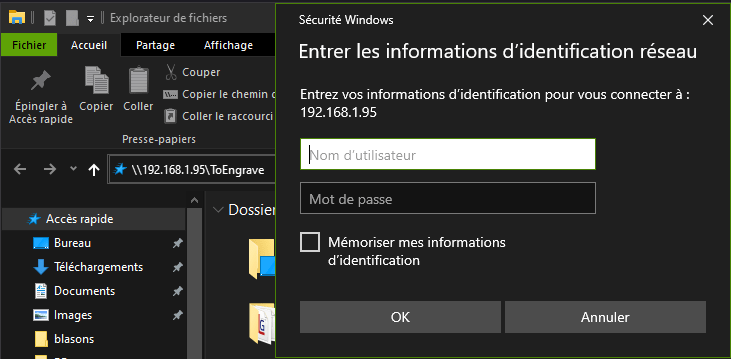
In Windows Explorer, enter the machine’s IP address, followed by the folder name \.
\\192.168.1.95\smbSharedFolder
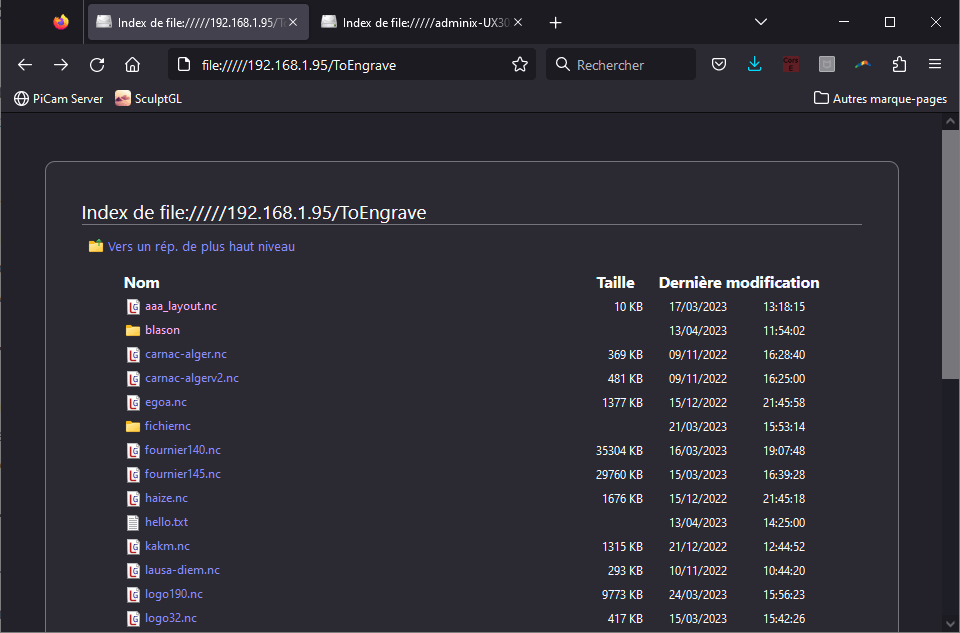
It is also possible to access the file using a web browser
Add a log file
It’s not necessary, but I advise you to add a log file so that you can monitor what’s happening with Samba, especially in the event of an error.
In the
Ajouter une section “global” au début du fichier et ajourer la ligne log file. Le paramètre “%m” spécifie de créer un fichier log pour chaque machine qui se connecte au dossier partagé Samba. Le paramètre log level à 1 permet d’activer le logging (defaut à 0).
[global]
log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m
log level = 1
[smbSharedFolder]
comment= Folder Shared by Samba Server
path = /home/<USERNAME>/smbSharedFolder
public = yes
read only = no
Use the Ctrl+X shortcut to save and close the file, then restart the service.
sudo systemctl restart smbd
To find the log file to view
ls /var/log/samba/
To read the log file
cat /var/log/samba/log.<IP_CLIENT>
Bonus: Access the folder using an Alias
Rather than using the IP address, it’s possible to define an alias for the machine. To do this, we’ll find the machine name and modify the file
To find the machine name
hostname
In the
sudo nano /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 MyMachine 192.168.1.95 MyMachine
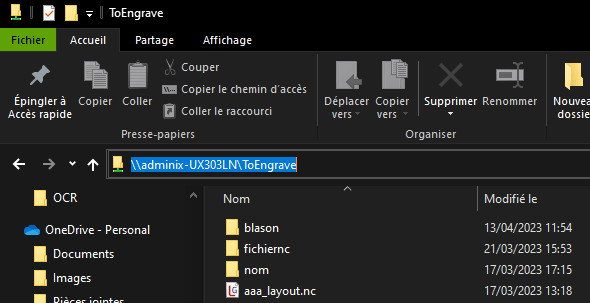
To access the folder, enter the following command in Windows Explorer
\MyMachine\smbSharedFolder
Once the alias has been defined, you can create a network location on your computer
In the This PC folder, right-click and select Add network location
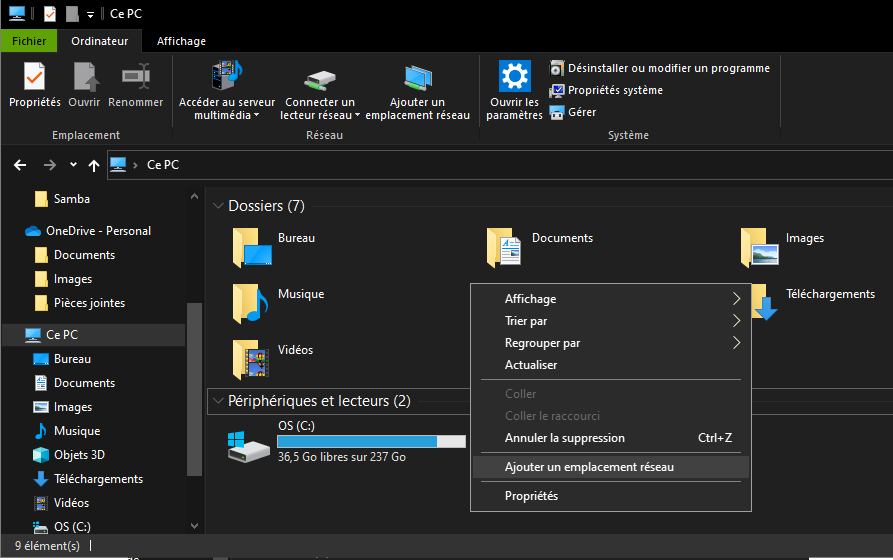
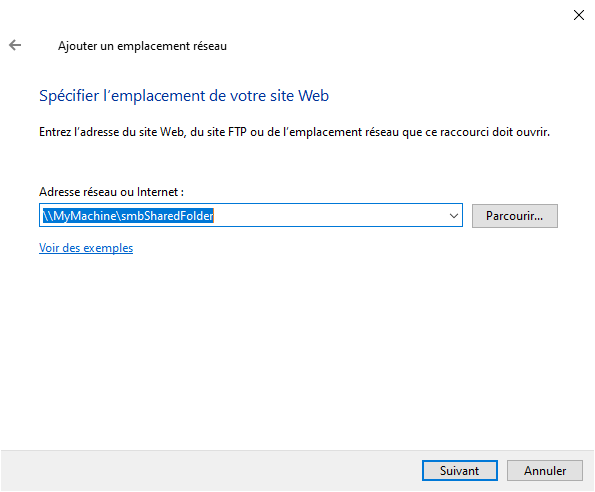
In the field specified the address of the shared folder
\MyMachine\smbSharedFolder
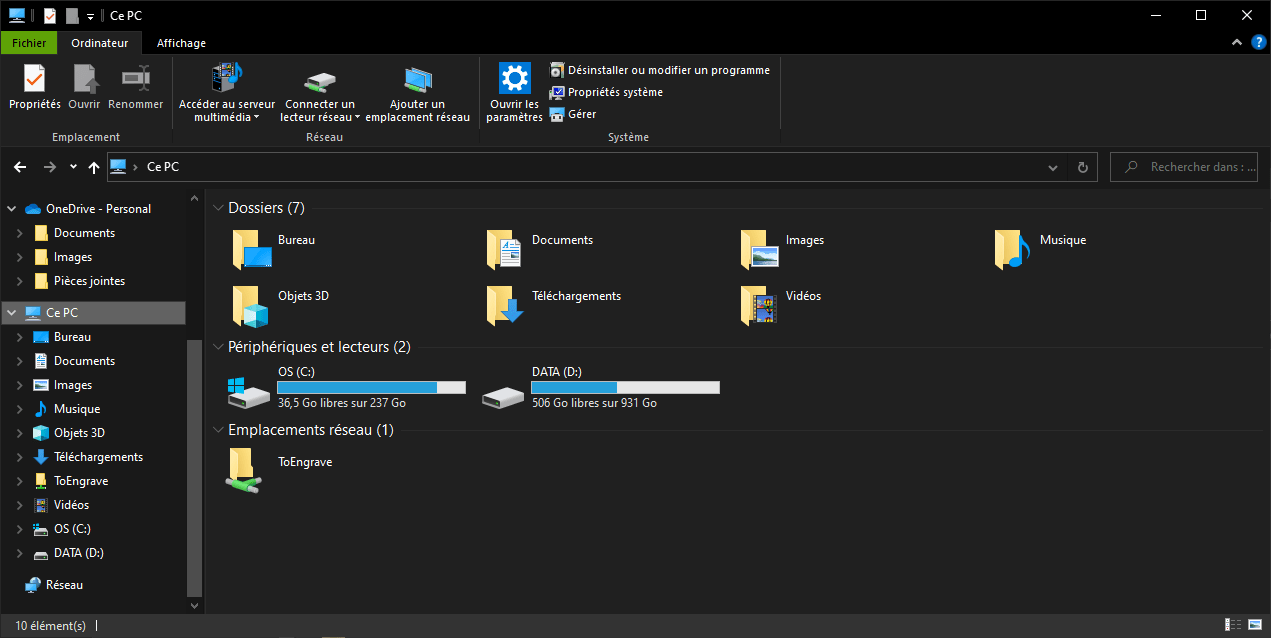
You can now access your shared folder directly from your Windows browser.
Samba installation and configuration file (Advanced users)
To make life easier, you can create a Samba installation file, which you can run on all your Linux installations.
Don’t forget to update the FOLDERNAME and USER names to match your needs.
sudo nano install_samba.sh chmod +x install_samba.sh sudo ./install_samba.sh
#folder user name
FOLDERNAME=sambashare
USER=pi
#install samba
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install samba -y
sudo systemctl stop smbd
#get machine info
HOSTNAME=$(hostname)
IPADDR=$(hostname -I | cut -f1 -d' ')
SMBVER=$(smbd --version)
#create samba folder
mkdir $FOLDERNAME
#save conf file for later
sudo mv /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb.conf.bak
#write conf file
#echo > /etc/samba/smb.conf
printf "[global]
#log file = /var/log/samba/log
log level = 1
[$FOLDERNAME]
comment= Folder Shared by Samba Server
path = /home/$USER/$FOLDERNAME
public = yes
read only = no
" > /etc/samba/smb.conf
#create host alias (optional)
echo $IPADDR $HOSTNAME >> /etc/hosts
#add user
sudo smbpasswd -a $USER
#start service
sudo systemctl restart smbd
#display result
echo --------------------- SUCCESS -----------------------
echo SAMBA $SMBVER was installed correcly
echo you can access your folder with
echo \\\\$IPADDR\\$FOLDERNAME
echo or
echo \\\\$HOSTNAME\\$FOLDERNAME
echo with username $USER
echo ------------------------------------------------------
N.B.: If this file doesn’t run correctly after copying and pasting, you can try using dos2unix to convert the file into a
Applications
- Access your files from anywhere with port forwarding
- Upload files from one machine to another on the same network
For example, I use it to transfer files from my Windows PC to my Linux PC, which manages my laser engraver.