One of the main objective in robotics is to make things move. A way to do that is to use servomotors. In this tutorial, we’ll see how to program your Raspberry Pi to control such a device.
Prerequisite: Programming with Raspberry Pi
Material
- Screen
- HDMI cable
- Keyboard
- Raspberry PI 3 (with OS on micro SD)
- Mouse
- Power supply micro USB B
- servomotor
Servomotor
Servomotors are small devices containing embedded mechanics and electronics. There are widely used in modelism, robotics and other applications. Their name comes from the fact that they control their position (or velocity) on their own.

Basically, a servomotor is composed with a small dc motor, a gearbox and embedded electronics that can be easily commanded using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) from a microcontroller.
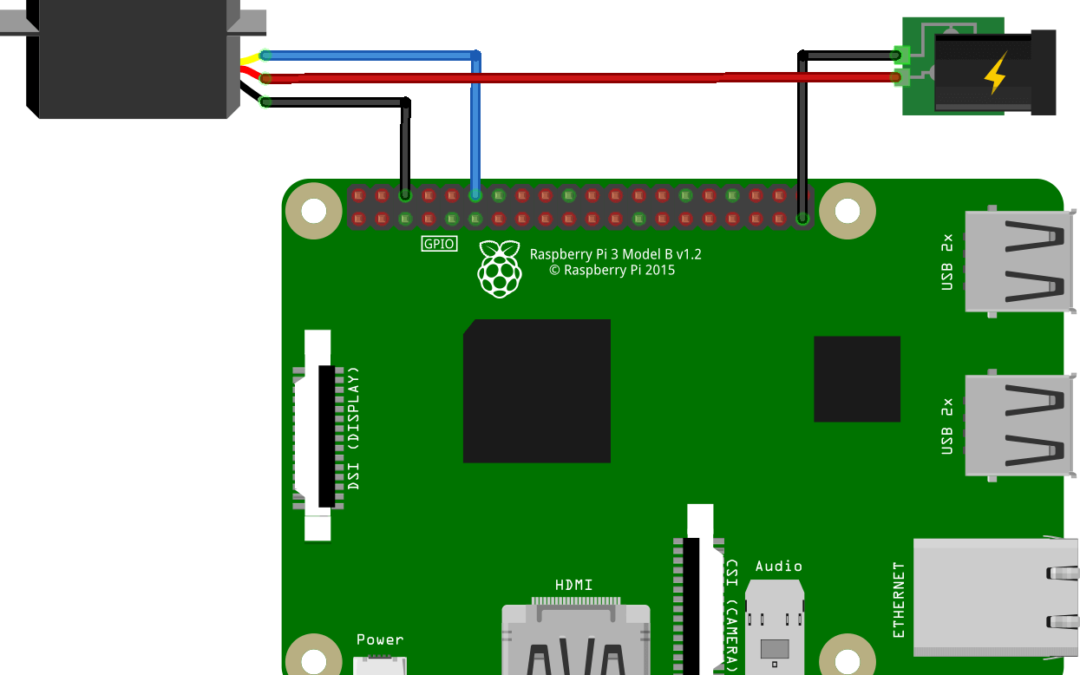
Wiring
Servomotor is powered through the black/brown cable (GND) and the red cable (+5V) and recieve the PWM signal on the yellow/white cable (pin12). Depending on the number of or power of servomotors you want to use, servomotor can be powered by the Raspberry Pi but it is advised to use an external power source.
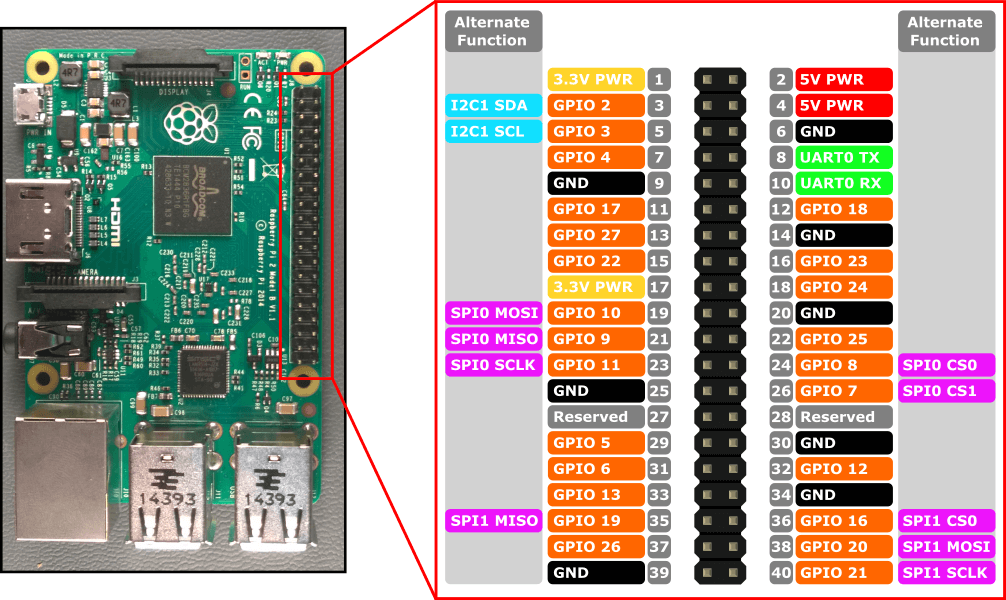
As a reminder, here is the pinout of the Raspberry Pi 3.
Basic code to control a servomotor
To control the servomotor in position, we only need to apply a PWM comand which is easily done using the RPi.GPIO library. To do so, we setup a pin as a PWM output.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
def AngleToDuty(ang):
return float(pos)/10.+5.
#Setup servoPin as PWM output of frequancy 100Hz
servoPin=12
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setup(servoPin,GPIO.OUT)
pwm=GPIO.PWM(servoPin,100)
#setup sweep parameters
depart =0
arrivee=180
DELAY=0.1
incStep=5
pos=depart
if __name__ == '__main__' :
pwm.start(AngleToDuty(pos)) #star pwm
nbRun=3
i=0
while i<nbRun:
print("--------------------------run {}".format(i))
for pos in range(depart,arrivee,incStep):
duty=AngleToDuty(pos)
pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(duty)
time.sleep(DELAY)
print("position: {}° -> duty cycle : {}%".format(pos,duty))
for pos in range(arrivee,depart,-incStep):
duty=AngleToDuty(pos)
pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(duty)
time.sleep(DELAY)
print("position: {}° -> duty cycle : {}%".format(pos,duty))
i=i+1
pwm.stop() #stop sending value to output
GPIO.cleanup() #release channel
N.B.: Becareful when copying Python code from the internet, you may encounter indentation issues which lead to compilation error.
Sources
Find other examples and tutorials in our Automatic code generator
Code Architect