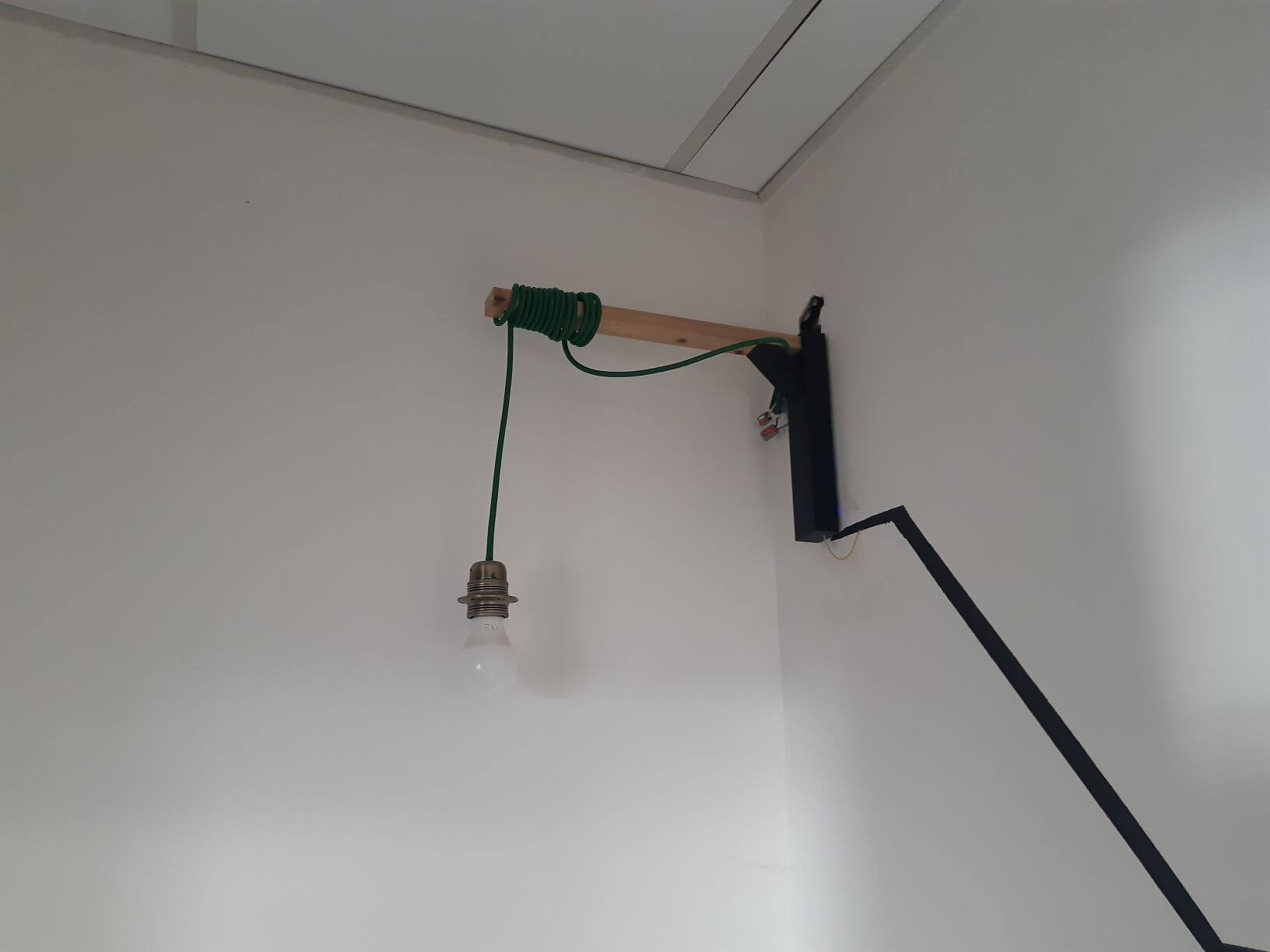
Una de las aplicaciones de los sensores capacitivos es la creación de un interruptor táctil para encender una lámpara, por ejemplo. En este proyecto vamos a diseñar un sensor capacitivo con Arduino que utilizaremos como interruptor táctil para encender y apagar una lámpara.
Hardware
- Arduino Nano
- Resistencia de 10M Ohm
- Relé
- cable eléctrico o material conductor
- Convertidor de CA
Esquema eléctrico
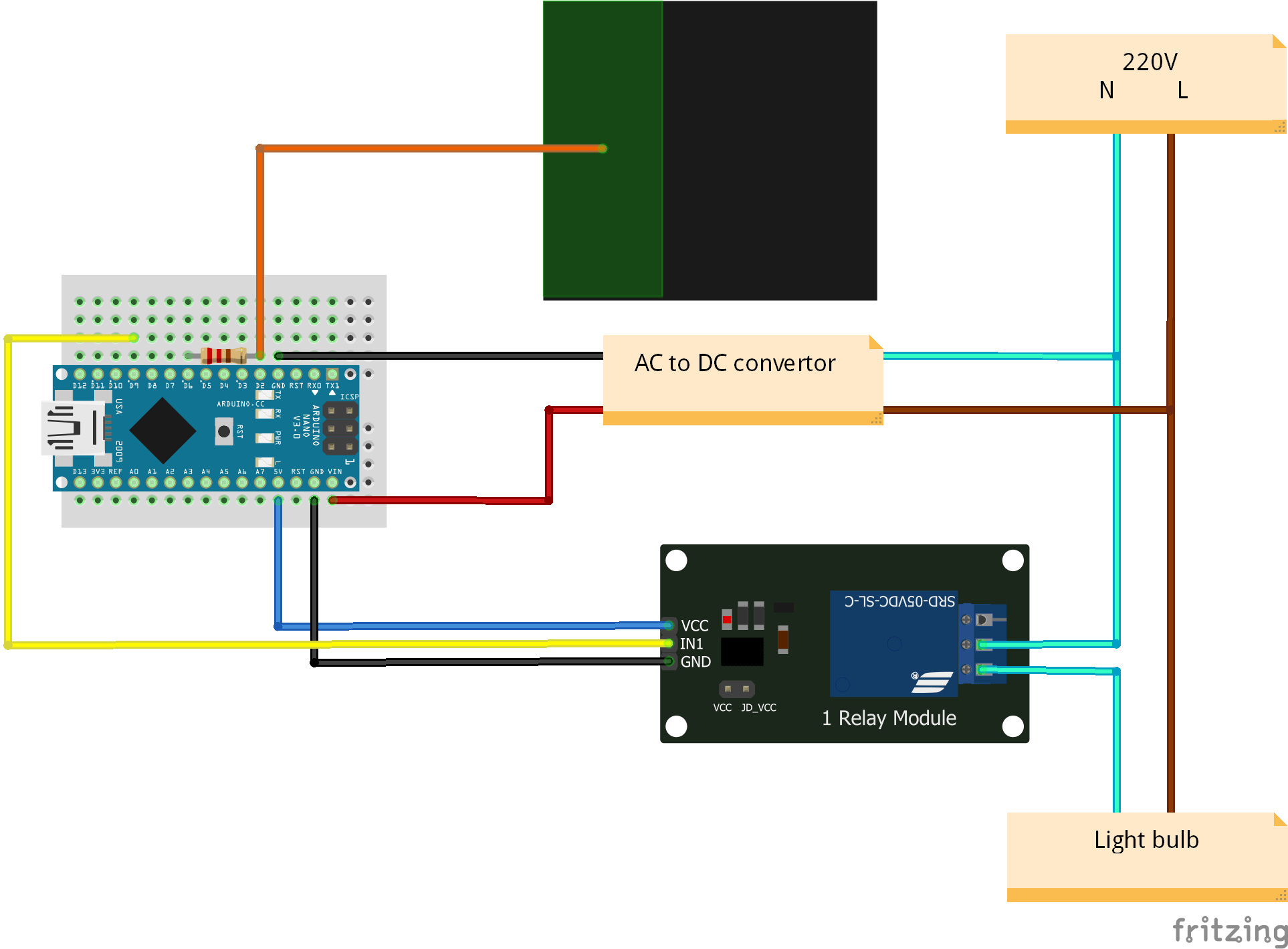
Atención: este proyecto utiliza 220V. Tome las precauciones necesarias para evitar electrocuciones.
Código
Para crear un sensor capacitivo, utilizamos la librería CapacitiveSensor. Cuando el sensor capacitivo cambia de estado, modificamos el estado enviado al relé para abrir o cerrar el circuito.
#include <CapacitiveSensor.h> #define DEBUG 0 //Capacitive sensor CapacitiveSensor cs_6_2 = CapacitiveSensor(6, 2); // 10M resistor between pins 6 & 2, pin 2 is sensor pin, add a wire and or foil if desired const int sensitivity = 50; long val; //Light const int lightPin = 9; bool lightState = false; bool btnState = false, oldState = false; //smooth long smoothval, total; const int numReadings = 3; long readings[numReadings] = {0}; int readIndex; long threshVal=500; void setup() { pinMode(lightPin, OUTPUT); cs_6_2.set_CS_AutocaL_Millis(0xFFFFFFFF); // turn off autocalibrate on channel 1 - just as an example Serial.begin(9600); Serial.println("Touchless lamp initialized"); delay(2000); for (int i = 0; i < numReadings; i++) { val = cs_6_2.capacitiveSensor(sensitivity);// increase for hi smoothval = smooth(val); } } void loop() { val = cs_6_2.capacitiveSensor(sensitivity);// increase for hi smoothval = smooth(val); if (DEBUG) { //Serial.print(millis() - timeStart); // check on performance in milliseconds Serial.print("\t"); // tab character for debug window spacing Serial.print(val); // print sensor output 1 Serial.print("\t"); Serial.print(smoothval); // print sensor smooth output Serial.println(); // print sensor smooth output } // condition if (btnState == false && smoothval > threshVal) { btnState = true; } if (btnState == true && smoothval <= threshVal*0.8) { btnState = false; } if (oldState != btnState) { if (oldState == false) { lightState = !lightState; } digitalWrite(lightPin, lightState); delay(200); } oldState = btnState; delay(100); // arbitrary delay to limit data to serial port } long smooth(long val) { /* function smooth */ ////Write data on device long average; // subtract the last reading: total = total - readings[readIndex]; // read from the sensor: readings[readIndex] = val;//cs.capacitiveSensor(sensitivity); // add the reading to the total: total = total + readings[readIndex]; // advance to the next position in the array: readIndex = readIndex + 1; // if we're at the end of the array... if (readIndex >= numReadings) { // ...wrap around to the beginning: readIndex = 0; } // calculate the average: average = total / numReadings; // send it to the computer as ASCII digits return average; }
Resultados
Al acercar la mano al cable que actúa como interruptor táctil, la lámpara debe encenderse o apagarse. De ti depende ajustar la sensibilidad del sensor, la resistencia y el valor umbral (umbralVal) para obtener el comportamiento deseado.
Próximos pasos
- Mejorar la robustez del sensor capacitivo frente a perturbaciones externas
- Añadir una función para apagar la lámpara automáticamente después de un cierto período de tiempo




