The SSH (Secure Socket Shell) protocol is widely used to connect to a remote server, or machine, connected to a network. It lets you exchange files, create, modify or run scripts on remote machines.
SSH is usually installed as standard in Linux or Windows distributions.
SSH protocol description
SSH (Secure Shell) is a cryptographic communication protocol used to establish secure, confidential connections between two computer systems over a network. Its principle is based on the use of asymmetric and symmetric encryption methods to protect data in transit between systems. User authentication is generally carried out using cryptographic key pairs, comprising a public key and a private key, ensuring secure verification of the user’s identity. SSH’s main utility lies in its role of securing remote access to servers, transferring secure files and managing systems remotely, offering robust protection against potential threats, including man-in-the-middle attacks and interception of sensitive data.
Open an SSH session
To connect to a device
ssh <host>@<serveur>
example for a raspberry pi
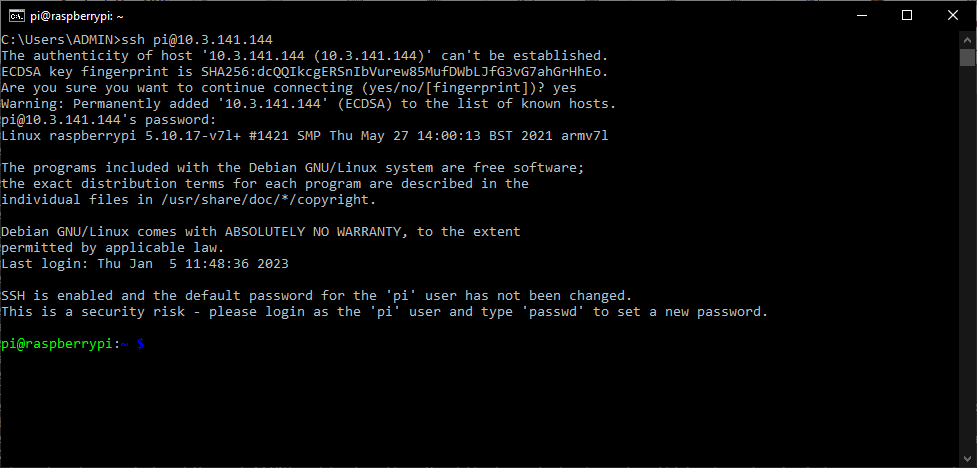
ssh pi@192.168.1.2
Once the connection has been established, the monitor will ask for the password to access the remote terminal.
If your remote machine supports it, the -X tag can be used to display your machine’s windows.
ssh -X <host>@<serveur>
Copy a remote file using the SSH protocol
La commande à utiliser pour copier un fichier d’une machine distante à une autre est la commande scp
scp <source> <destination>
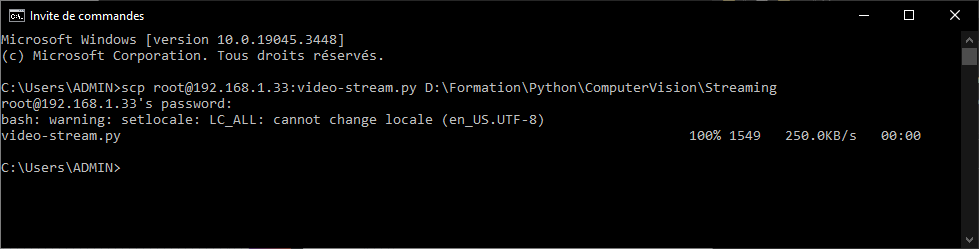
scp root@192.168.1.33:script.py C:\Users\ADMIN
A password will be requested to validate the copy.
Login with password
On Linux, you can install and use SSH
sudo apt-get install sshpass
sshpass -p {password} ssh {user}@{ipaddress}
On Windows, Putty can take care of password management.
Install PuTTy, then add the executable folder to the Path environment variable (C:\Program Files\PuTTY).
putty -ssh "root@192.168.1.32" -pw root #pour ouvrir une connexion en directe
To send live orders, we use plink
plink -ssh <username>@<host> -pw <password> <command>
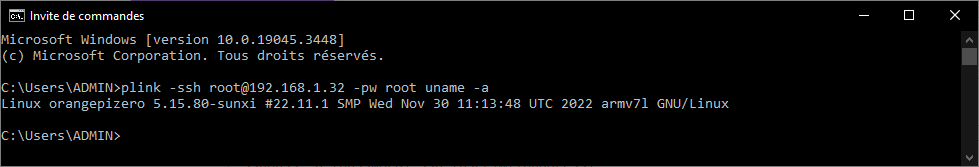
Example
plink -ssh root@192.168.1.32 -pw root uname -a
Using Python to send SSH commands
We use the subprocess library to execute terminal commands
import subprocess
subprocess.Popen(f"ssh {user}@{host} {cmd}", shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE).communicate()
Sending SSH commands requiring a password via Python
python3 -m pip install paramiko
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
#ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy()) #if missing
ssh.connect(server, username=username, password=password)
ssh_stdin, ssh_stdout, ssh_stderr = ssh.exec_command("uname -a")
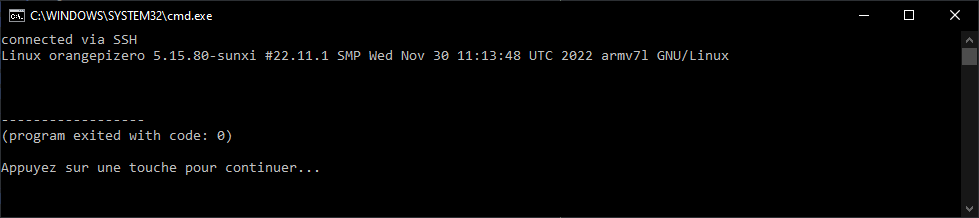
print("connected via SSH")
print(ssh_stdout.read().decode())
ssh.close()