Para probar y utilizar el protocolo MQTT, puede instalar un servidor MQTT utilizando Mosquitto en un ordenador Windows o Linux. Una aplicación común es instalar Mosquittoen una Raspberry Pi y utilizarla como servidor MQTT para IoT y domótica.
Descripción del protocolo MQTT
El protocolo MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport) es un protocolo de comunicaciones especificado para pequeños intercambios de datos a través de redes con grandes retardos y poco ancho de banda.
El protocolo consiste en un servidor MQTT (broker) al que se conectan los clientes. Los clientes pueden publicar o suscribirse a un tema. Los mensajes publicados en temas pueden intercambiarse entre clientes.
Mosquittoes un servidor MQTT de código abierto que facilita el uso del protocolo MQTT entre distintos dispositivos conectados a la misma red.
Instalación del servidor MQTT en Linux
En Linux, Mosquittopuede instalarse utilizando los siguientes comandos
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install mosquitto mosquitto-clientsUna vez instalado el servicio, puede gestionarse mediante los siguientes comandos
sudo systemctl stop mosquitto #arrêter
sudo systemctl start mosquitto #démarrer
sudo systemctl restart mosquitto #redémarrer
sudo systemctl status mosquitto #connaitre le statusEl servidor se configura mediante el archivo
sudo nano /etc/mosquitto/mosquitto.conf
sudo nano /etc/mosquitto/conf.d/default.confEjemplo de fichero de configuración
# Place your local configuration in /etc/mosquitto/conf.d/ # # A full description of the configuration file is at # /usr/share/doc/mosquitto/examples/mosquitto.conf.example pid_file /var/run/mosquitto/mosquitto.pid persistence true persistence_location /var/lib/mosquitto/ log_dest file /var/log/mosquitto/mosquitto.log port 1883 allow_anonymous true include_dir /etc/mosquitto/conf.d
Instalación del servidor MQTT en Windows
En Windows, descargue e instale Mosquitto
Una vez instalado, introduzca el siguiente comando en un símbolo del sistema para iniciar el servicio
mosquittoPara comprobar que el servicio se ha iniciado:
netstat -an | find str 1883C:\Users\ADMIN>netstat -an | findstr 1883
TCP 127.0.0.1:1883 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP [::1]:1883 [::]:0 LISTENINGEl archivo de configuración del servidor se encuentra en la carpeta de instalación
C:\Program Files\mosquitto\mosquitto.confProbar MQTT
Puede utilizar mosquitto directamente desde la línea de comandos. En un terminal, introduzca el siguiente comando
mosquitto_sub -h localhost -t test_topicEn otro terminal
mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t test_topic -m "Hello World!"N.B.: Ejecute el código de abonado antes que el código de editor
Probar MQTT avec Python
En el siguiente ejemplo, vamos a utilizar mosquitto con Python para intercambiar mensajes MQTT entre dos scripts python
python -m pip install paho-mqttScript Python de abonado
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt #import library
import time
MQTT_BROKER = "localhost" #specify the broker address, it can be IP of raspberry pi or simply localhost
MQTT_TOPIC = "test_channel" #this is the name of topic
global messageReceived
messageReceived=False
# callback called when client receives a CONNACK response
def on_connect(client, userdata, flags, rc):
if rc==0:
client.subscribe(MQTT_TOPIC)
print("subscribe to {}".format(MQTT_TOPIC))
else:
syslog.syslog("bad connection {}".format(rc))
# callback called when a PUBLISH message is received
def on_message(client, userdata, msg):
print(msg.topic+" "+str(msg.payload.decode("utf-8")))
global messageReceived
messageReceived=True
client = mqtt.Client()
client.on_connect = on_connect
client.on_message = on_message
client.connect(MQTT_BROKER)
client.loop_forever()# use this line if you don't want to write any further code. It blocks the code forever to check for data
"""
client.loop_start() #use this line if you want to write any more code here
delay=0.001
counter=120/delay #2min
while messageReceived==False and counter>0:
time.sleep(delay)
client.loop_stop()
"""
Script editor Python
Para publicar en un tema, basta con especificar la dirección del servidor (MQTT_BROKER) y el nombre del tema en el que se desea publicar (MQTT_TOPIC).
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt #import library
import time
MQTT_BROKER = "localhost"
MQTT_TOPIC = "test_channel"
client = mqtt.Client("pyScript")
client.connect(MQTT_BROKER)
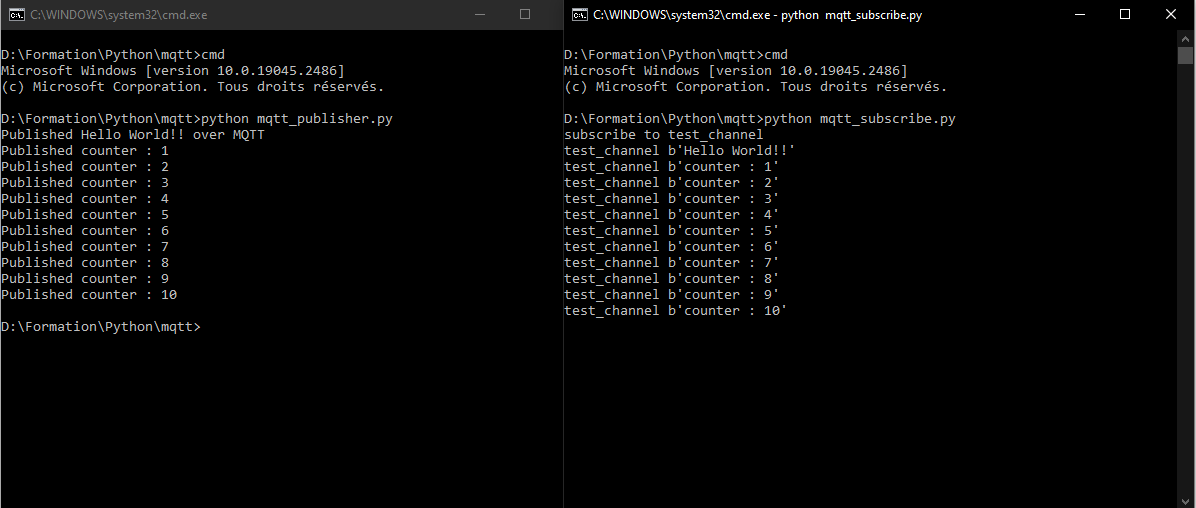
msg="Hello World!!"
client.publish(MQTT_TOPIC,msg)
print("Published {} over MQTT".format(msg))
counter=0
while counter<10:
counter+=1
client.publish(MQTT_TOPIC,"counter : {}".format(counter))
print("Published counter : {}".format(counter))
time.sleep(0.001)
client.disconnect()
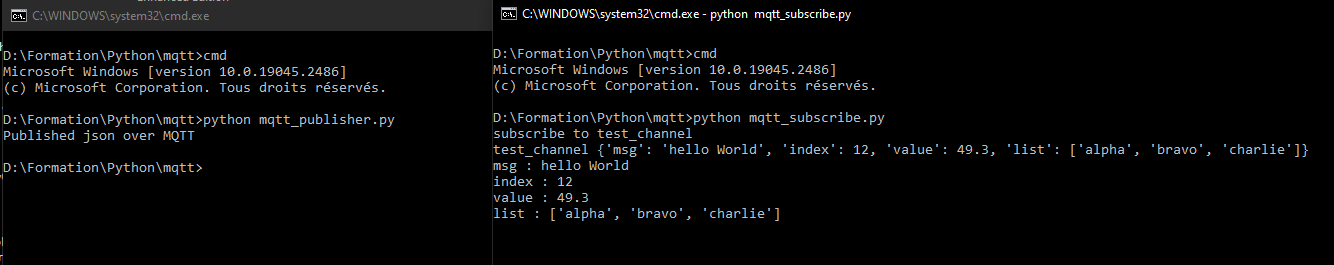
Enviar un grupo de datos ordenados mediante JSON
El paquete JSON de python es una práctica biblioteca para almacenar e intercambiar datos en forma de archivos JSON.
Script para enviar un JSON
El archivo JSON está simplemente en formato «diccionario».
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt #import library
import time
import json
MQTT_BROKER = "localhost"
MQTT_TOPIC = "test_channel"
client = mqtt.Client("10.3.141.1")
client.connect(MQTT_BROKER)
json_data = {}
json_data['msg'] = "hello World"
json_data['index'] = 12
json_data['value'] = 49.3
json_data['list'] = ["alpha","bravo","charlie"]
client.publish(MQTT_TOPIC,str(json_data))
print("Published json over MQTT")
Script para recibir un JSON
En el script de recepción, añadiremos la decodificación del json en forma de diccionario
if "{" in msgrec: #decode json
data = json.loads(msgrec.replace("'",'"'))
for key in data:
print("{} : {}".format(key,data[key]))
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt #import library
import time
import json
MQTT_BROKER = "localhost" #specify the broker address, it can be IP of raspberry pi or simply localhost
MQTT_TOPIC = "test_channel" #this is the name of topic
global messageReceived
messageReceived=False
# The callback for when the client receives a CONNACK response from the server.
def on_connect(client, userdata, flags, rc):
if rc==0:
client.subscribe(MQTT_TOPIC)
print("subscribe to {}".format(MQTT_TOPIC))
else:
syslog.syslog("bad connection {}".format(rc))
# The callback for when a PUBLISH message is received from the server.
def on_message(client, userdata, msg):
msgrec=str(msg.payload.decode("utf-8"))
print(msg.topic+" "+msgrec)
if "{" in msgrec: #decode json
data = json.loads(msgrec.replace("'",'"'))
for key in data:
print("{} : {}".format(key,data[key]))
global messageReceived
messageReceived=True
client = mqtt.Client()
client.on_connect = on_connect
client.on_message = on_message
client.connect(MQTT_BROKER)
client.loop_forever()